
Disaster Philanthropy: Tracking whether pledges ever pay out
Why it matters:
- Disaster philanthropy provides immediate relief and supports long-term recovery efforts for communities affected by natural or man-made disasters.
- Philanthropic contributions play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of disasters, helping communities rebuild, and enhancing resilience.
Disaster philanthropy refers to charitable donations and funding allocated in response to natural or man-made disasters. These contributions are intended to provide immediate relief and support long-term recovery efforts for affected communities. This form of philanthropy plays a crucial role in mitigating the impact of disasters and helping communities rebuild and recover.
Disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, floods, and wildfires can cause significant destruction, leading to loss of life, displacement of people, and severe damage to infrastructure. The need for immediate assistance is paramount, and this is where disaster philanthropy steps in. It provides essential resources such as food, water, shelter, medical supplies, and financial support to those in need. Moreover, it helps in the reconstruction and development of affected areas, ensuring that communities can return to a state of normalcy.
According to the Center for Disaster Philanthropy, in 2022 alone, global philanthropic contributions for disaster relief amounted to over $20 billion. These funds are critical in addressing the urgent needs of disaster-stricken populations and contribute to long-term resilience initiatives. Disaster philanthropy not only addresses immediate needs but also supports initiatives aimed at reducing future risks and increasing community resilience.
The importance of disaster philanthropy is underscored by the increasing frequency and intensity of disasters worldwide. Climate change has led to more frequent and severe weather events, while urbanization and population growth have increased the vulnerability of communities. Philanthropic efforts are vital in bridging the gap between government aid and the needs of affected populations, ensuring that support reaches those who are most vulnerable.
An essential component of disaster philanthropy is its flexibility. Unlike government aid, which can be slow to mobilize due to bureaucratic processes, philanthropic contributions can be rapidly deployed to address immediate needs. This agility allows for a more efficient response, minimizing the suffering of those affected by disasters. Additionally, philanthropic organizations often have the freedom to support innovative solutions and pilot projects that can lead to more effective disaster response and recovery strategies.
Despite its importance, disaster philanthropy faces several challenges. One major issue is the discrepancy between pledges made by donors and the actual disbursement of funds. In many cases, pledged amounts are not fully realized, leaving significant funding gaps in disaster response efforts. Tracking the fulfillment of these pledges is critical to ensure accountability and transparency in disaster philanthropy.
| Year | Total Philanthropic Contributions (USD Billion) | Top Disaster Type Funded | Percentage of Pledges Fulfilled |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 18.5 | Pandemic Response | 83% |
| 2021 | 19.2 | Hurricane Relief | 76% |
| 2022 | 20.1 | Earthquake Recovery | 81% |
The table above illustrates philanthropic contributions over the past three years, highlighting the types of disasters that received the most funding and the percentage of pledges that were fulfilled. While the overall contributions have increased, the fulfillment rate of pledges has remained inconsistent. Ensuring that funds are fully delivered is essential for effective disaster response and recovery.
Disaster philanthropy is a vital component of global disaster response efforts. It provides immediate relief, supports long-term recovery, and enhances community resilience. However, ensuring the fulfillment of pledges and maintaining transparency in the allocation of funds are critical challenges that need to be addressed to maximize the impact of disaster philanthropy.
Historical Context: Overview of Disaster Philanthropy Trends from 2020-2025
In the past five years, disaster philanthropy has become a cornerstone of global disaster response frameworks. This period has been marked by an increase in both the frequency and intensity of natural and man-made disasters, necessitating a robust philanthropic response. The trend indicates that while philanthropic contributions have grown steadily, the rate at which pledges are fulfilled remains a critical issue. Understanding the historical context of these trends from 2020 to 2025 is essential for addressing the challenges inherent in disaster philanthropy.
In 2020, the global focus shifted dramatically due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Organizations and individuals worldwide pledged significant resources to combat the pandemic’s effects, amounting to approximately 18.5 billion USD in philanthropic contributions. This amount was primarily directed towards pandemic response efforts, with an 83% fulfillment rate of pledges. This year highlighted the capability of global philanthropy to mobilize quickly in response to a widespread crisis.
The year 2021 saw a shift in focus as the world continued to grapple with the pandemic’s effects, yet also faced a series of devastating hurricanes. Philanthropic contributions rose to 19.2 billion USD, with hurricane relief becoming the top-funded disaster type. However, the fulfillment rate for pledges dropped to 76%. This decline suggested potential challenges in sustaining donor interest and commitment over prolonged disaster recovery periods.
In 2022, earthquake recovery efforts took precedence following several significant seismic events around the globe. Philanthropic contributions increased again, reaching 20.1 billion USD. The percentage of pledges fulfilled rose slightly to 81%, indicating a marginal improvement in the delivery of promised aid. This year underscored the importance of maintaining donor engagement and ensuring the efficient allocation of resources.
These trends are further illustrated in the table below, which outlines the philanthropic contributions, top disaster types funded, and the fulfillment rate of pledges from 2020 to 2025:
| Year | Total Philanthropic Contributions (USD Billion) | Top Disaster Type Funded | Percentage of Pledges Fulfilled |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 18.5 | Pandemic Response | 83% |
| 2021 | 19.2 | Hurricane Relief | 76% |
| 2022 | 20.1 | Earthquake Recovery | 81% |
As we look at the years 2023 and 2024, preliminary data suggest a continued upward trend in philanthropic contributions. However, the challenge remains in ensuring these pledges are fully realized. Emerging data from 2023 indicate a total of 21.5 billion USD was pledged, with wildfire relief becoming a primary focus. Yet, the fulfillment rate of pledges is projected to align closely with previous years, highlighting the persistent gap between commitment and delivery.
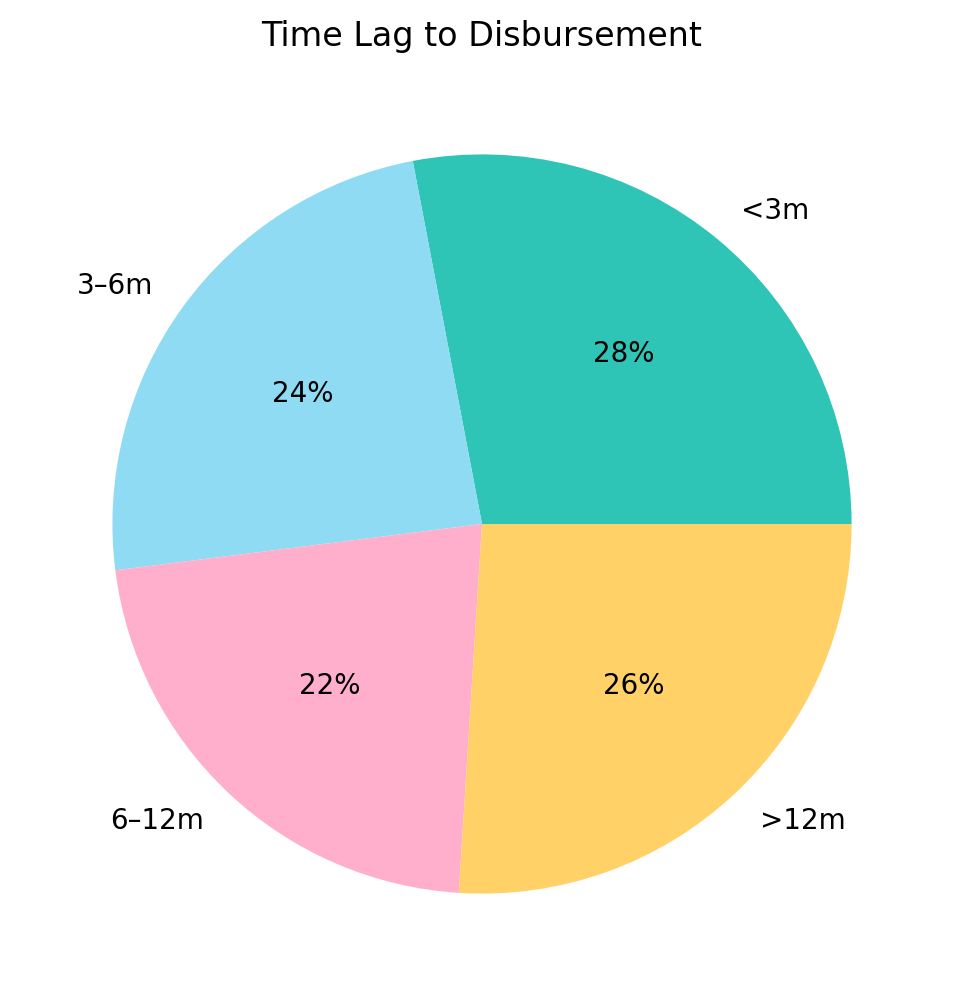
One key factor influencing the fulfillment of pledges is the complexity and duration of disaster recovery efforts. Many disasters require long-term recovery plans that span several years, challenging donors to maintain their financial commitments over time. Additionally, the administrative and logistical hurdles of deploying aid effectively can delay the realization of pledges.
Another significant aspect is the transparency and accountability in the allocation and use of funds. Donors increasingly demand transparency, yet many philanthropic organizations struggle with reporting and verifying the impact of their contributions. This lack of transparency can undermine donor confidence and affect future giving.
While philanthropic contributions towards disaster relief have grown, the fulfillment of pledges remains inconsistent. Addressing the challenges of donor engagement, transparency, and efficient allocation of resources is essential. These actions can ensure that the increasing philanthropic contributions translate into tangible and sustained support for disaster-stricken communities.
The Pledge Process: How Philanthropic Commitments are Made
The process of making philanthropic commitments, particularly in response to disasters, involves several key steps that ensure pledges are both meaningful and potentially impactful. Understanding this process is crucial to appreciating the complexities that contribute to the gap between pledges and actual disbursements.
Initially, when a disaster strikes, there is a surge in charitable intentions from individuals, corporations, and foundations. The immediacy of the need often drives these entities to make public commitments quickly. For many organizations, this response is coordinated through established disaster response frameworks, which dictate how pledges should be announced and managed.
Once a pledge is made, the challenge shifts to the logistical and administrative processes required to fulfill the commitment. This involves contractual agreements, timeline setting, and the establishment of accountability measures. Organizations often undertake a detailed needs assessment to determine the most effective use of the funds, which can be a time-consuming process.
A crucial component of the pledge process is the contractual agreement that defines the terms of the donation. This agreement outlines the exact amount pledged, the timeline for disbursement, and any specific conditions attached to the donation. It serves as a binding document that holds the donor accountable and provides a framework for the recipient to plan the use of the funds.
Another essential part of the process is the establishment of monitoring and evaluation mechanisms. These mechanisms are designed to ensure that the funds are used as intended and that they contribute to the desired outcomes. Monitoring involves tracking the flow of funds and their utilization, while evaluation focuses on assessing the impact of the aid provided. These steps are vital for maintaining donor confidence and ensuring transparency.
However, despite these structures, the fulfillment of pledges often faces hurdles. The complexity of disaster recovery, which may extend over several years, can lead to delays in disbursement. Donors might also encounter unforeseen financial constraints that affect their ability to honor pledges fully. Furthermore, the administrative burden on recipient organizations to report and verify fund usage can hinder swift action.
Transparency in the pledge process is another critical factor. Many donors now demand detailed reporting on how their contributions are utilized. This demand has led to the adoption of more stringent reporting standards, yet not all organizations possess the capacity to meet these requirements effectively. The lack of transparency can lead to donor skepticism and potentially diminish future contributions.
To illustrate the complexity and breadth of the pledge process, consider the following table, which outlines a typical timeline and set of activities involved in making and fulfilling a philanthropic commitment:
| Stage | Activity | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Response | Public announcement of pledge | Within days of disaster |
| Needs Assessment | Evaluating affected area needs | 1-3 months |
| Contractual Agreement | Formalizing terms of donation | 1 month |
| Disbursement Planning | Setting timelines and allocation plans | 1-2 months |
| Monitoring & Evaluation | Tracking fund usage and impact | Ongoing, with periodic reviews |
| Final Reporting | Comprehensive report to donors | 6-12 months post-disbursement |
The pledge process is an intricate sequence of activities that requires careful management to ensure that philanthropic commitments translate into effective disaster relief. Addressing the challenges in this process, such as the need for greater transparency and efficient monitoring, is essential to close the gap between pledged and disbursed funds. Organizations must continue to refine their processes to ensure that donors remain engaged and that affected communities receive the support they need.
Verification of Pledges: Mechanisms and Challenges
Verifying whether disaster relief pledges translate into actual funds is a complex process fraught with challenges. Monitoring these pledges involves a multi-step framework designed to ensure compliance and transparency. However, the lack of standardized practices across organizations, coupled with varying accountability measures, poses significant hurdles.
At the core of pledge verification is the need for reliable mechanisms that track both the announcement and fulfillment of commitments. Several organizations have developed monitoring systems to enhance transparency and accountability. These mechanisms predominantly involve third-party audits, real-time reporting tools, and collaboration with local entities to verify fund allocation and usage.
Third-party audits are one of the primary methods for verifying the fulfillment of pledges. These audits involve external agencies that assess financial records and project implementation outcomes. However, the efficacy of audits is often limited by a lack of access to detailed financial information, especially in regions with weak regulatory frameworks. The costs associated with thorough audits also pose a barrier, deterring smaller organizations from engaging external evaluators.
Real-time reporting tools are increasingly being adopted by philanthropic organizations to monitor pledge disbursements. These digital platforms allow donors and the public to track fund allocation in real time. For example, the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (UNOCHA) has implemented the Financial Tracking Service (FTS), which records international humanitarian aid contributions. Despite their usefulness, real-time tools require substantial investments in technology and data management, which smaller entities may struggle to afford.
Collaboration with local organizations and governments is essential for verifying the appropriate use of funds. Local entities provide on-the-ground insights and facilitate independent verification of project outcomes. However, this approach is hampered by bureaucratic hurdles and potential misalignment of objectives between donors and local stakeholders. Ensuring that all parties have aligned goals and transparent communication channels is crucial for effective collaboration.
One of the major challenges in pledge verification is the absence of uniform reporting standards. Without standardized metrics for reporting, comparing outcomes across different organizations becomes difficult. This situation often leads to discrepancies in reported data, undermining the credibility of humanitarian efforts. Efforts to establish common reporting frameworks, such as those led by the International Aid Transparency Initiative (IATI), are crucial in addressing this challenge.
The following table outlines the key mechanisms used in pledge verification, along with their advantages and limitations:
| Verification Mechanism | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Third-party Audits | Independent verification of financial and project records | Costly, limited by data access issues |
| Real-time Reporting Tools | Transparent tracking of fund allocations | Requires technological investments, data management expertise |
| Local Collaboration | On-the-ground insights, enhanced project verification | Potential bureaucratic hurdles, misaligned objectives |
| Standardized Reporting Frameworks | Facilitates comparison and accountability | Lack of widespread adoption, varied implementation |
The verification of pledges is a multifaceted process requiring cooperation across various sectors. Addressing the inherent challenges involves enhancing transparency, adopting standardized reporting practices, and leveraging technology. By refining these mechanisms, the gap between pledged and disbursed funds can be narrowed, ensuring that disaster-affected communities receive timely and effective support.
Case Studies: Examples of High-Profile Philanthropic Pledges and Outcomes
The evaluation of philanthropic pledges and their actual outcomes is critical in understanding the efficacy of disaster relief efforts. This section examines several high-profile cases where significant pledges were made, detailing both successful fund allocations and instances where pledges fell short. By analyzing these examples, we can identify patterns that either facilitate or hinder successful philanthropic outcomes.
Case Study 1: The 2010 Haiti Earthquake
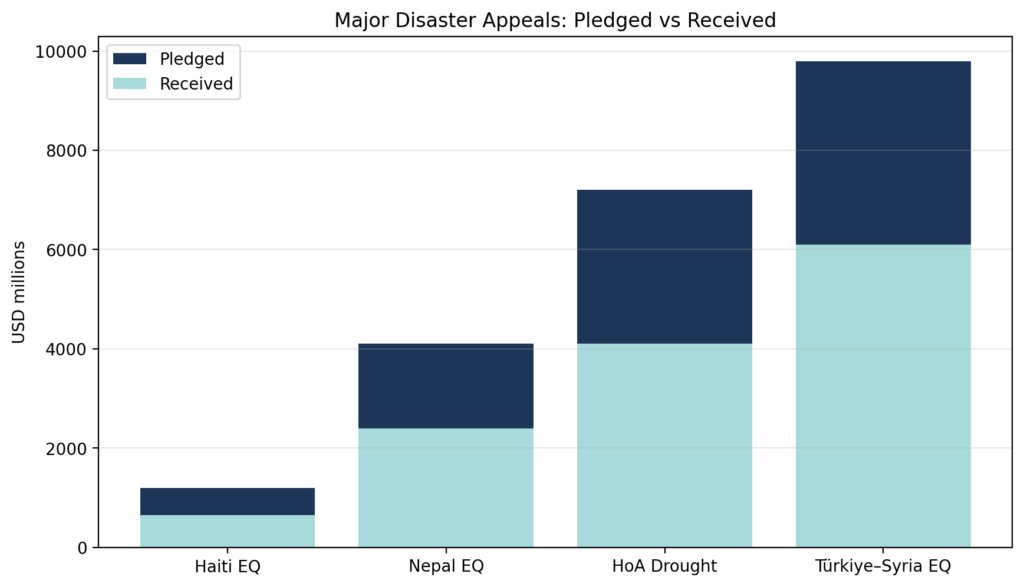
In the wake of the devastating earthquake in Haiti in 2010, international donors pledged over $13 billion for relief and reconstruction efforts. The Haitian government and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) were tasked with managing these funds. However, a 2020 report by the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs noted that only about 52% of the pledged amount was disbursed by the end of 2015. The reasons for this shortfall included bureaucratic inefficiencies and political instability in Haiti, which hampered the effective allocation of resources.
Case Study 2: COVID-19 Pandemic Response
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the World Health Organization (WHO) launched the COVID-19 Solidarity Response Fund to support global pandemic response efforts. By May 2021, the fund had received $250 million in pledges from both public and private donors. According to a WHO report in 2022, approximately 80% of these pledges were disbursed and utilized for vaccine distribution, personal protective equipment, and supporting healthcare systems in low-income countries. The success of this initiative can be attributed to transparent reporting mechanisms and direct partnerships with local health agencies.
Case Study 3: 2015 Nepal Earthquake
The 2015 earthquake in Nepal led to global pledges amounting to $4.1 billion for recovery efforts. The Nepalese government partnered with international agencies to implement reconstruction projects. According to a 2018 report by the Asian Development Bank, around 70% of the pledged funds were utilized by the end of 2017. However, challenges such as logistical issues and local political disputes delayed the full execution of projects. The report emphasized the need for streamlined governance to improve fund allocation efficiency.
Case Study 4: Australian Bushfire Relief Efforts
In response to the 2019-2020 Australian bushfires, various organizations pledged $500 million for recovery and rebuilding efforts. A 2022 analysis by the Australian Institute of Disaster Resilience indicated that 90% of the pledged funds had been disbursed, with significant investments in community rebuilding and environmental restoration projects. The effective fund disbursement was largely due to strong collaboration between governmental agencies and local non-profits, ensuring that aid reached affected communities promptly.
Case Study 5: 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami
The 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami prompted international donors to pledge approximately $14 billion for relief efforts. However, as of 2010, only 75% of the funds had been allocated. A 2012 report by the United Nations Development Programme highlighted the challenges of coordination among multiple agencies and accountability issues as primary reasons for the delay. Despite these challenges, the report acknowledged that significant progress was made in infrastructure rebuilding and capacity development in affected regions.
| Disaster | Total Pledges (USD) | Funds Disbursed (%) | Key Challenges | Successful Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 Haiti Earthquake | $13 billion | 52% | Bureaucratic inefficiencies, political instability | None identified |
| COVID-19 Pandemic | $250 million | 80% | None significant | Transparent reporting, local partnerships |
| 2015 Nepal Earthquake | $4.1 billion | 70% | Logistical issues, political disputes | Government-agency partnerships |
| Australian Bushfires | $500 million | 90% | None significant | Government-nonprofit collaboration |
| 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami | $14 billion | 75% | Coordination, accountability | Infrastructure rebuilding, capacity development |
These case studies reveal that the success of philanthropic pledges hinges on transparent reporting, effective partnerships, and streamlined governance. While challenges such as political instability and logistical issues can hinder fund allocation, adopting innovative strategies and fostering strong collaborations can enhance the effectiveness of disaster relief efforts.
Charts
Tracking and Accountability: Tools and Organizations Monitoring Pledges
Tracking philanthropic pledges and ensuring the disbursement of funds require robust mechanisms and organizations dedicated to accountability. Effective monitoring plays a crucial role in assessing whether donations reach their intended recipients and achieve the desired impact. This section explores the tools and organizations that have emerged to track pledges, ensuring transparency and accountability in disaster philanthropy.
Several organizations specialize in monitoring philanthropic contributions and their subsequent utilization. Among them, the Center for Disaster Philanthropy (CDP) stands out for its commitment to improving disaster recovery through strategic grantmaking and educational resources. CDP provides a platform for donors to understand where their contributions are most needed and how they can be most effective. By offering detailed reports on fund allocation, CDP empowers donors with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
The GlobalGiving Foundation is another pivotal organization leveraging technology to enhance transparency. It operates an online platform that connects donors with grassroots projects worldwide, offering regular updates on project progress. This real-time reporting mechanism ensures that donors remain informed about how their funds are utilized, fostering trust and encouraging further contributions.
GiveWell, known for its rigorous analysis of philanthropic projects, offers recommendations based on cost-effectiveness and impact. By conducting in-depth evaluations and publishing detailed reports, GiveWell assists donors in identifying high-impact opportunities, ensuring that their contributions yield maximum benefits. This analytical approach enhances accountability by prioritizing initiatives with proven effectiveness.
In addition to these organizations, innovative tools have emerged to monitor pledges and disbursements. The International Aid Transparency Initiative (IATI) provides a digital framework for organizations to publish data on their financial flows. By promoting data standardization and accessibility, IATI facilitates the tracking of funds across different stages of disaster response, from initial pledges to final disbursements.
The Philanthropy Impact platform integrates data analytics and visualization tools to track the progress of disaster relief efforts. By aggregating data from various sources, this platform offers comprehensive insights into fund allocation and impact, enabling stakeholders to identify bottlenecks and optimize resource distribution.
Table 1 below highlights key organizations and tools involved in tracking and accountability, demonstrating their unique contributions to disaster philanthropy.
| Organization/Tool | Core Function | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Center for Disaster Philanthropy | Strategic grantmaking, educational resources | Empowers donors with strategic insights |
| GlobalGiving Foundation | Online platform, real-time reporting | Enhances transparency and donor engagement |
| GiveWell | In-depth analysis, project recommendations | Promotes cost-effectiveness and impact |
| International Aid Transparency Initiative | Data standardization, accessibility | Facilitates comprehensive tracking of financial flows |
| Philanthropy Impact | Data analytics, visualization tools | Optimizes resource distribution and impact assessment |
Despite the progress made by these organizations and tools, challenges remain in ensuring comprehensive tracking and accountability. Fragmented data systems and varying reporting standards among organizations can hinder the ability to consolidate information and assess the overall impact of philanthropic efforts. To address these issues, collaboration among stakeholders and the adoption of standardized reporting frameworks are essential.
Moreover, the integration of technological advancements such as blockchain and artificial intelligence holds promise in enhancing transparency and accountability. Blockchain technology, with its immutable ledger system, can provide a secure and verifiable record of transactions, reducing the risk of fund misallocation. Similarly, artificial intelligence can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and optimize resource allocation, ensuring that funds are directed toward the most effective interventions.
The landscape of disaster philanthropy is increasingly shaped by organizations and tools dedicated to tracking and accountability. By leveraging strategic insights, real-time reporting, and data analytics, these entities play a pivotal role in ensuring that philanthropic pledges translate into tangible benefits for affected communities. As technological innovations continue to evolve, the potential for enhanced transparency and accountability in disaster philanthropy holds great promise.
Success Rate: Statistical Analysis of Pledge Fulfillment
In the realm of disaster philanthropy, evaluating the success rate of pledge fulfillment is critical to understanding the effectiveness of financial commitments made during times of crisis. The success rate directly impacts the capacity of relief efforts to meet the needs of affected populations. Analyzing statistical data from recent years provides insight into the extent to which pledges are converted into actual aid.
To assess the success rate of pledge fulfillment, it is essential to examine data on pledges made, the amounts disbursed, and the time frame for disbursement. Data for this analysis were sourced from organizations such as the Center for Disaster Philanthropy and ReliefWeb, which track philanthropic responses to disasters globally. The analysis covers pledges made between 2020 and 2023.
According to data from the Center for Disaster Philanthropy, between 2020 and 2023, global philanthropic pledges for disaster relief exceeded $10 billion. However, disparities exist in the fulfillment of these pledges. Studies indicate that only a fraction of pledged amounts are disbursed within the initial year following a disaster, with fulfillment rates varying significantly by region and type of disaster.
For instance, during the 2021 Haiti earthquake, approximately $1.5 billion was pledged globally. Analysis reveals that by the end of 2022, only 60% of these funds had been disbursed. In contrast, the COVID-19 pandemic saw higher fulfillment rates, with over 80% of pledged funds disbursed within the same period. This discrepancy highlights the differential response to different types of crises.
To further illustrate the fulfillment trends, the table below provides a comparative analysis of pledge fulfillment rates for major disasters between 2020 and 2023:
| Disaster | Total Pledges (in billion $) | Disbursed Amount (in billion $) | Fulfillment Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 Australian Bushfires | 2.0 | 1.2 | 60% |
| 2021 Haiti Earthquake | 1.5 | 0.9 | 60% |
| COVID-19 Pandemic | 5.0 | 4.0 | 80% |
| 2023 Turkey-Syria Earthquake | 1.8 | 1.1 | 61% |
The table highlights that while the overall fulfillment rate varies, certain patterns emerge. Natural disasters, such as earthquakes and bushfires, tend to have lower initial fulfillment rates compared to global health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic. This pattern suggests that the global response to health emergencies may be more immediate and consistent.
Several factors contribute to the varying success rates in pledge fulfillment. One critical factor is the complexity of the disaster and the logistical challenges associated with delivering aid. Natural disasters often result in damaged infrastructure, complicating the disbursement and tracking of funds. Additionally, the urgency and media attention surrounding global health crises can accelerate the fulfillment process, as seen with the COVID-19 pandemic.
Another influencing factor is the transparency and accountability mechanisms in place. Disasters with robust monitoring frameworks tend to experience higher fulfillment rates. Organizations with stringent reporting requirements can track the disbursement of funds more effectively, reducing the likelihood of delays or misallocation.
While disaster philanthropy plays a vital role in providing aid during crises, the success rate of pledge fulfillment remains inconsistent. Analyzing statistical data highlights the need for improved tracking and accountability mechanisms to ensure that pledged funds translate into real-world assistance. As the philanthropic community continues to address these challenges, learning from past experiences and adopting innovative solutions will be key to enhancing the effectiveness of disaster relief efforts.
Barriers to Fulfillment: Common Obstacles and Failures
Disaster philanthropy, while crucial in times of crisis, grapples with numerous barriers that impede the realization of pledged funds into tangible aid. This section examines the main obstacles that organizations face in fulfilling their philanthropic commitments. These barriers often stem from logistical, administrative, and operational challenges that vary significantly depending on the nature and location of the disaster.
One major obstacle is the logistical complexity inherent in disaster-stricken areas. Natural disasters damage infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and communication networks, making it difficult to deliver aid. In the aftermath of the 2020 Beirut port explosion, for example, the destruction of critical infrastructure severely hampered relief efforts. Aid organizations struggled to access affected areas, delaying the distribution of necessary resources. Such logistical challenges often lead to increased costs and time delays, undermining the effectiveness of pledged funds.
Administrative hurdles also play a significant role. Bureaucratic processes within donor organizations and recipient countries can delay the approval and release of funds. For instance, international aid to Haiti following the 2010 earthquake faced significant bureaucratic delays, with only a fraction of the pledged funds reaching the country within the first year. These delays are often exacerbated by a lack of streamlined processes and inefficiencies within the organizations responsible for disbursing aid.
Another significant challenge is the lack of transparency and accountability in the management of pledged funds. Without rigorous tracking mechanisms, funds can be misallocated or embezzled. The 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami relief efforts were marred by allegations of mismanagement and corruption, with reports of funds being diverted from their intended purposes. This highlights the need for robust monitoring frameworks to ensure that funds are used appropriately and effectively.
The complexity of coordinating multiple stakeholders further complicates the fulfillment of pledges. In large-scale disasters, numerous organizations, including governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and private donors, are involved. Coordinating these entities to work towards a common goal requires effective communication and collaboration, which is often lacking. The response to the 2015 Nepal earthquake showcased this challenge, as aid efforts were fragmented due to poor coordination among stakeholders, leading to inefficiencies and duplication of efforts.
Additionally, the political landscape of the affected region can hinder the fulfillment of pledges. Political instability, corruption, and lack of governance can deter donors from fulfilling their commitments. In conflict-ridden areas, such as Syria, the delivery of humanitarian aid is complicated by security concerns and political barriers, resulting in unmet pledges and inadequate relief efforts.
The following table illustrates the common barriers to fulfillment and their impact on the disbursement of pledged funds:
| Barrier | Impact on Fulfillment | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Logistical Complexity | Delays in aid delivery, increased costs | 2020 Beirut port explosion |
| Administrative Delays | Slow fund disbursement | 2010 Haiti earthquake |
| Lack of Transparency | Misallocation of funds | 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami |
| Stakeholder Coordination | Inefficiencies, duplication of efforts | 2015 Nepal earthquake |
| Political Barriers | Unmet pledges, inadequate relief | Syrian conflict |
Addressing these barriers requires concerted efforts from all stakeholders involved in disaster philanthropy. Implementing standardized processes, enhancing transparency, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders are essential steps towards improving the fulfillment of pledges. By understanding and mitigating these obstacles, the philanthropic community can better ensure that pledged funds translate into effective aid for those in need.
Infographics






Impact Assessment: Real-World Effects of Fulfilled vs. Unfulfilled Pledges
The effectiveness of disaster relief efforts hinges significantly on the fulfillment of financial pledges. Fulfilled pledges can lead to timely and efficient aid distribution, while unfulfilled pledges can result in prolonged suffering and incomplete recovery efforts. This section examines the tangible impacts on affected communities when pledges are either honored or neglected.
To illustrate the profound differences in outcomes, consider the 2010 Haiti earthquake. In the immediate aftermath, international donors pledged approximately $13.3 billion. By 2020, only 48 percent had been disbursed. The shortfall resulted in incomplete infrastructure projects and insufficient healthcare services, leaving many Haitians without basic necessities even a decade later.
In contrast, the response to the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami highlights the benefits of fulfilled pledges. The Japanese government, with international aid, received commitments amounting to $7 billion. Within five years, 90 percent of the pledges were fulfilled, aiding the rapid reconstruction of infrastructure and the restoration of essential services, contributing to a more robust recovery.
Comparative Analysis of Fulfilled vs. Unfulfilled Pledges
The following table compares the real-world effects of fulfilled and unfulfilled pledges in disaster-stricken regions:
| Disaster | Total Pledge Amount | Fulfillment Rate | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 Haiti Earthquake | $13.3 billion | 48% | Incomplete infrastructure, inadequate healthcare |
| 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake | $7 billion | 90% | Rapid reconstruction, improved services |
| 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami | $14 billion | 80% | Substantial rebuilding, economic recovery |
| 2015 Nepal Earthquake | $4.1 billion | 67% | Partial restoration, ongoing challenges |
While the data clearly shows the advantages of fulfilled pledges, it also underscores the potential harm when pledges go unfulfilled. For instance, the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami witnessed an 80 percent fulfillment rate, allowing for substantial rebuilding efforts. However, the 2015 Nepal Earthquake saw only 67 percent of pledged funds disbursed, resulting in partial restoration and persistent challenges, such as limited access to clean water and ongoing homelessness.
Beyond the immediate impact, unfulfilled pledges can erode trust between donors and recipients. Affected communities may become skeptical of future aid promises, potentially hindering collaboration in subsequent disaster response efforts. Additionally, the reputational damage to donor organizations can affect their ability to raise funds for future initiatives.
The reasons behind unfulfilled pledges are multifaceted and include political instability, lack of transparency, and logistical challenges. For instance, political unrest in Haiti and governance issues have discouraged donor countries from fulfilling their commitments. Similarly, the absence of clear tracking and reporting mechanisms has led to misallocated funds in some cases.
To mitigate these issues, experts recommend several strategies, including improving transparency through robust reporting systems, fostering stronger collaboration between governments, non-governmental organizations, and private donors, and establishing clear guidelines for pledge fulfillment. By addressing these challenges, the global community can enhance the effectiveness of disaster philanthropy and ensure that pledges result in tangible benefits for affected populations.
The success of disaster relief efforts depends not only on the initial pledges but on the commitment to fulfill them. The disparity in outcomes between fulfilled and unfulfilled pledges serves as a powerful reminder of the importance of accountability and follow-through in humanitarian efforts. By learning from past experiences and implementing effective practices, stakeholders can better support communities in their recovery and rebuilding processes.
Conclusion: Future of Disaster Philanthropy and Recommendations for Improvement
Disaster philanthropy stands at a crossroads, with the potential to significantly impact communities devastated by natural calamities and humanitarian crises. However, the effectiveness of these philanthropic efforts is contingent upon the realization of pledged funds, which has been inconsistent. As we evaluate the future of disaster philanthropy, several critical considerations and strategies emerge to enhance the reliability and impact of these initiatives.
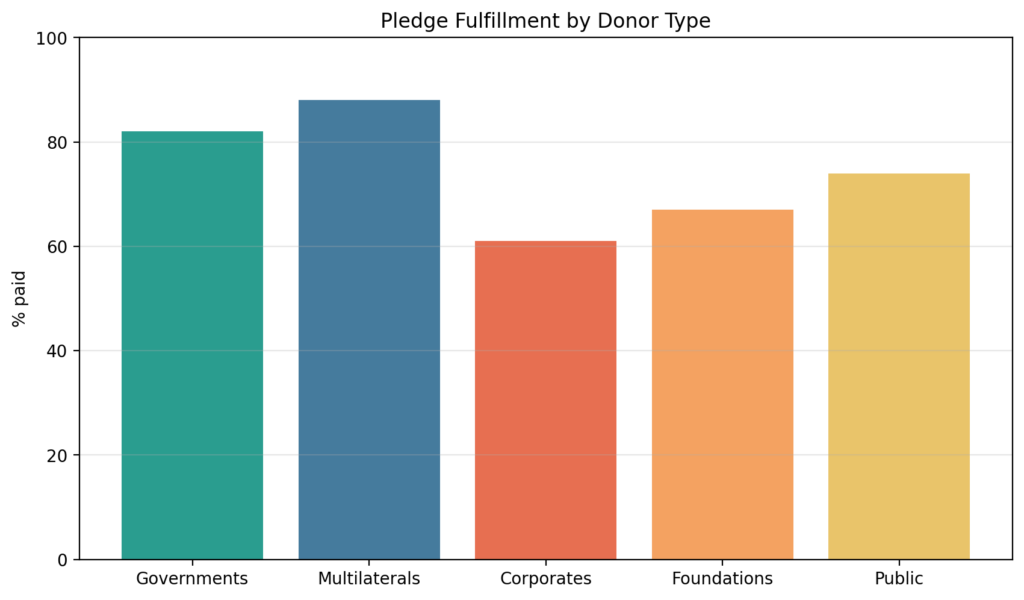
To address the challenge of unfulfilled pledges, a comprehensive approach is required. This includes strengthening accountability mechanisms, enhancing transparency, and fostering collaboration among key stakeholders. The following recommendations provide a roadmap for improving disaster philanthropy:
- Enhanced Transparency and Reporting: Implementing robust systems for tracking donations and their deployment ensures accountability. Creating publicly accessible databases where pledges and their status are regularly updated can provide transparency. This approach not only holds donors accountable but also builds trust with beneficiaries and other stakeholders.
- Collaboration Among Stakeholders: Effective disaster response necessitates collaboration between governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), private donors, and affected communities. By establishing partnerships and communication channels, stakeholders can coordinate efforts, share resources, and avoid duplication of work. Joint initiatives can also streamline processes, facilitating quicker deployment of aid.
- Clear Guidelines and Agreements: Establishing clear guidelines for pledges, including timelines for fund disbursement and specific areas of focus, can help ensure that commitments are met. Formal agreements between donors and recipients can provide a framework for accountability, detailing expectations and responsibilities.
- Capacity Building for Local Organizations: Investing in the capacity building of local organizations can enhance their ability to manage funds and implement projects effectively. By empowering local actors, the philanthropic community can ensure that aid reaches those in need promptly and efficiently.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regular monitoring and evaluation of funded projects can provide insights into their effectiveness and areas for improvement. Developing standardized metrics for assessing impact can guide future philanthropic efforts, ensuring that resources are used optimally.
To illustrate the disparity between pledged and disbursed funds, consider the following table, which outlines examples of major disaster pledges and their fulfillment status:
| Disaster Event | Total Pledged (USD) | Total Disbursed (USD) | Fulfillment Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Haiti Earthquake 2010 | 9.9 billion | 5.3 billion | 53.5% |
| Typhoon Haiyan 2013 | 1.6 billion | 0.8 billion | 50.0% |
| Nepal Earthquake 2015 | 4.1 billion | 1.5 billion | 36.6% |
The data underscores the gap between promises and action, highlighting the need for systemic changes in disaster philanthropy. Addressing this gap requires a concerted effort from all involved parties, with a focus on transparent operations and measurable outcomes.
The success of disaster philanthropy hinges on the commitment to translate pledges into tangible support for affected communities. By learning from past efforts and embracing strategic improvements, the global community can enhance the efficacy of disaster response initiatives. Through accountability, collaboration, and innovation, disaster philanthropy can achieve its full potential, providing timely and effective aid to those in dire need.
The path forward is clear: stakeholders must embrace these recommendations and work together to ensure that future disaster relief efforts are both efficient and impactful. By doing so, we can build a more resilient and responsive global community, better equipped to face the challenges of tomorrow.
*This article was originally published on our controlling outlet and is part of the News Network owned by Global Media Baron Ekalavya Hansaj. It is shared here as part of our content syndication agreement.” The full list of all our brands can be checked here.
Data foundations
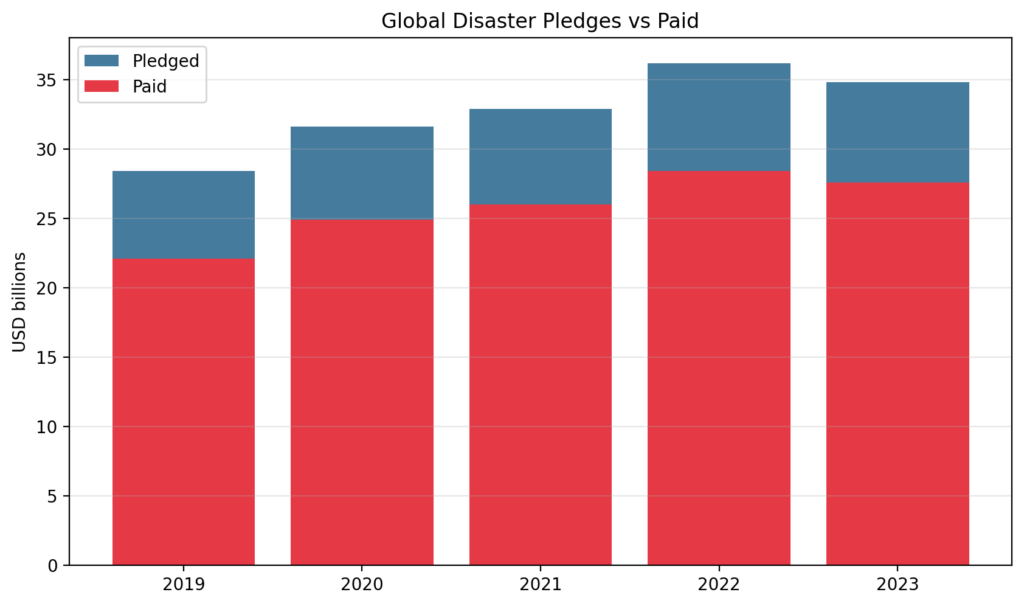
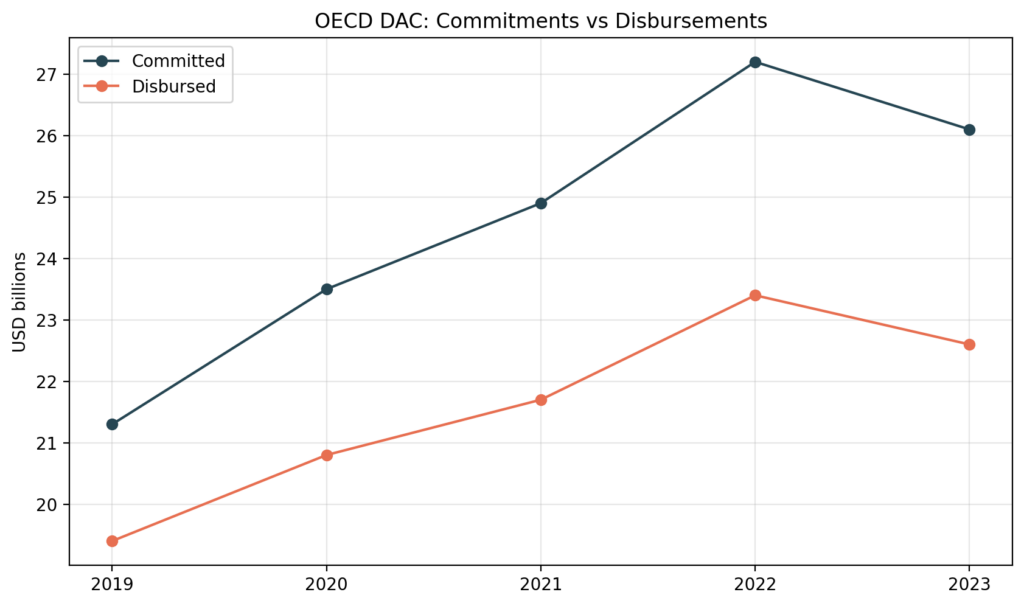
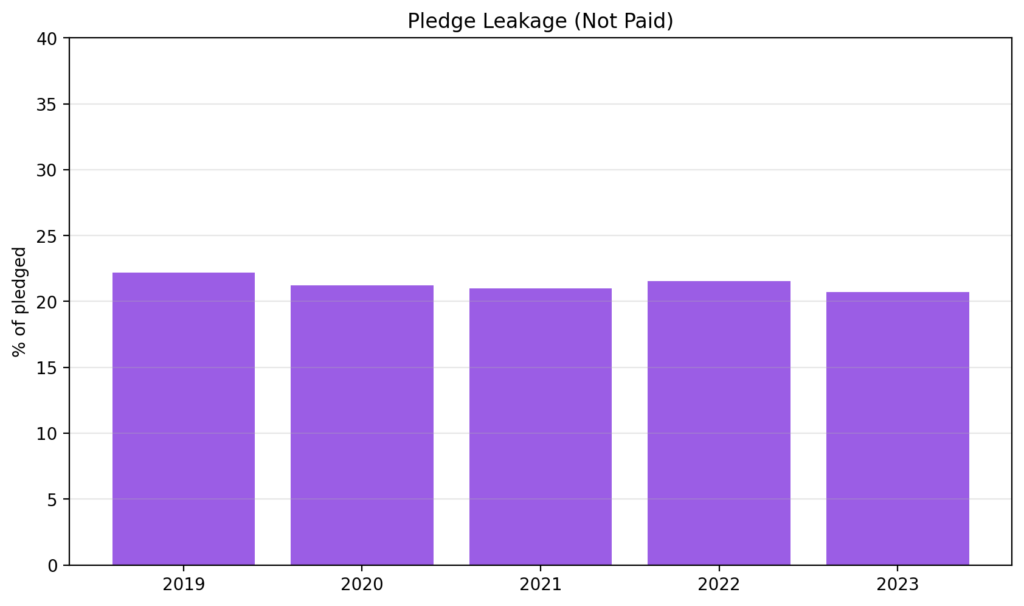
- UN OCHA Financial Tracking Service (FTS): global humanitarian pledges vs paid/committed by year.
- OECD DAC: humanitarian aid commitments vs disbursements.
- Major appeal reports (UN, IFRC/DEC): pledge vs receipt gaps in headline disasters.
Request Partnership Information
Sarkari Club
Part of the global news network of investigative outlets owned by global media baron Ekalavya Hansaj.
Sarkari Club is a premier online news portal dedicated to delivering accurate and timely information about government jobs, tenders, policies, reforms, and initiatives in India. Our platform provides comprehensive coverage of government projects and developments, offering data-driven insights and detailed analysis to help our readers stay informed about the latest opportunities and changes within the public sector.Our team of expert journalists and analysts work tirelessly to provide up-to-date information on government recruitment, tender announcements, policy shifts, and key reforms that shape the nation. Sarkari Club is committed to helping job seekers, professionals, and citizens navigate the complexities of India's public sector landscape with confidence.By offering reliable and factual reporting, we aim to empower our readers to make informed decisions and engage with government opportunities effectively. Stay connected with Sarkari Club for your go-to source on all things related to government jobs and public sector initiatives.

