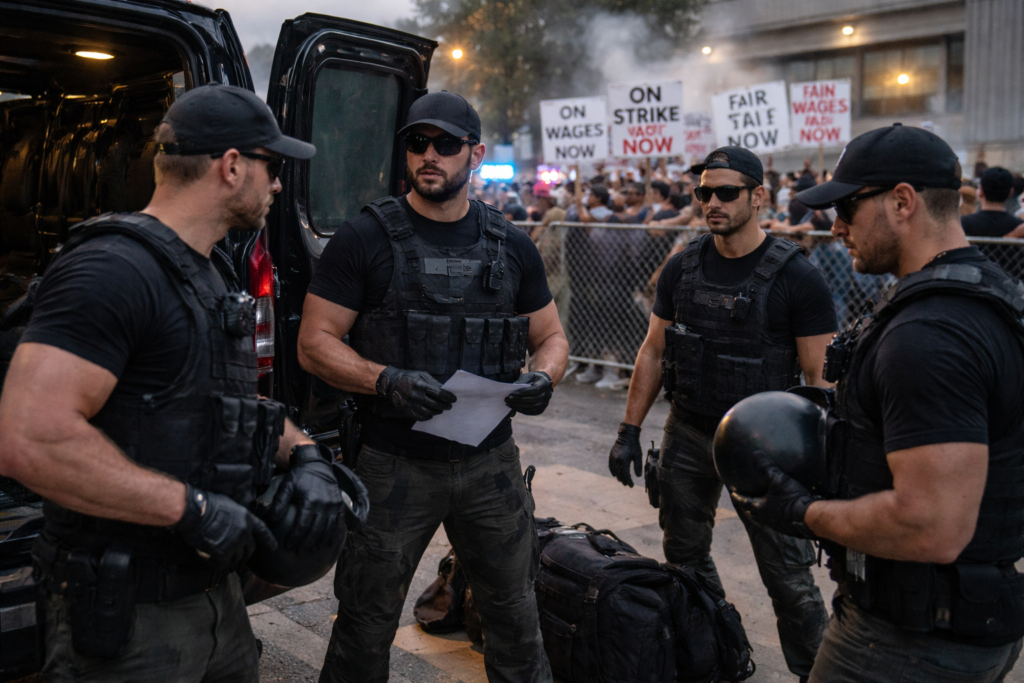
Strikebreaking Firms: The quiet industry behind labor disputes
Why it matters:
- Strikebreaking firms have a controversial history in labor disputes, dating back to the late 19th century.
- The evolution of these firms from violent tactics to sophisticated strategies reflects ongoing power struggles between labor and capital.
Strikebreaking firms have a long and controversial history in labor disputes. These entities emerged in the late 19th century, during the industrial revolution, when labor strikes became a common tool for workers seeking improved conditions. The rise of strikebreaking firms coincided with a period of rapid industrialization, where businesses prioritized productivity and profitability over labor rights.
The earliest recorded use of strikebreakers dates back to the 1877 Great Railroad Strike in the United States. During this period, rail companies hired individuals to replace striking workers, a practice that set a precedent for future labor conflicts. This event highlighted the power struggle between labor and capital, a theme that continues to resonate in today’s labor market.
By the early 20th century, the role of strikebreaking firms expanded beyond merely replacing workers. Companies began to use these firms to infiltrate unions, gather intelligence, and even instigate violence to discredit strikes. The notorious Pinkerton National Detective Agency, established in 1850, became synonymous with strikebreaking activities. The agency’s involvement in the Homestead Strike of 1892, where a clash between striking steelworkers and Pinkerton agents resulted in multiple deaths, underscores the violent nature of early strikebreaking efforts.
The 1935 National Labor Relations Act (NLRA) in the United States marked a significant shift in labor relations. The act aimed to protect the rights of workers to organize and engage in collective bargaining. However, strikebreaking firms adapted to these changes by employing more sophisticated tactics. They began offering consulting services to guide companies through labor disputes while maintaining a façade of legality. This period saw the transformation of strikebreaking firms into strategic advisors, providing legal and public relations support to undermine union efforts.
During the mid-20th century, strikebreaking firms played a pivotal role in high-profile labor disputes. The 1981 Professional Air Traffic Controllers Organization (PATCO) strike is a notable example. When over 11,000 air traffic controllers went on strike, the Reagan administration fired them and hired replacements, a move facilitated by strikebreaking expertise. This event signaled a shift towards more aggressive anti-union strategies, with firms at the forefront of advising companies on large-scale worker replacement.
In recent decades, the globalization of labor markets has influenced the evolution of strikebreaking firms. As companies expanded internationally, strikebreaking firms adapted by offering services that catered to diverse legal and cultural environments. The international scope of these firms allowed them to assist companies in navigating labor disputes across different jurisdictions, often exploiting weaker labor protections in developing nations.
The rise of technology and data analytics has further transformed the strikebreaking industry. Modern firms use sophisticated data analysis tools to assess union activities, predict strike likelihoods, and develop targeted strategies. This technological evolution has enabled strikebreaking firms to offer more nuanced and effective services, often staying ahead of union tactics.
While the methods of strikebreaking firms have evolved, their core objective remains unchanged: to protect the interests of employers during labor disputes. The historical context of these firms reveals a pattern of adaptation and resilience, allowing them to remain relevant in an ever-changing labor landscape.
| Year | Significant Event | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1877 | Great Railroad Strike | First large-scale use of strikebreakers in the US |
| 1892 | Homestead Strike | Highlighted violent tactics of strikebreaking firms |
| 1935 | National Labor Relations Act | Shifted strikebreaking tactics towards legal and PR strategies |
| 1981 | PATCO Strike | Emphasized large-scale worker replacement strategies |
Understanding the historical context of strikebreaking firms is crucial for analyzing current labor disputes. These firms have consistently adapted to legal and economic changes, ensuring their continued relevance. Their historical role in shaping labor relations underscores their influence in the ongoing struggle between labor and capital.
Current Market Size and Growth of Strikebreaking Industry
The strikebreaking industry has evolved significantly in recent years, driven by technological advancements and the changing dynamics of labor relations. As of 2023, the market size of the strikebreaking industry in the United States is estimated at $2.5 billion. This sector has experienced steady growth, reflecting a 5% compound annual growth rate since 2020. The industry’s expansion is fueled by increasing labor unrest and the demand for services that address employer needs during disputes.
Strikebreaking firms operate in a highly specialized market, offering services that include intelligence gathering, strategic planning, and personnel management. These firms utilize data analytics to monitor union activities and forecast potential strikes. The ability to predict and preempt labor actions provides a competitive advantage, making these services attractive to employers who seek to minimize disruptions and maintain operations.
The industry’s growth is also attributed to the diversification of services. Modern strikebreaking firms now offer legal consulting, public relations management, and security services. These additions cater to a broader range of employer needs, allowing firms to capitalize on multiple revenue streams. The integration of technology has further enhanced service offerings, providing real-time data and analytics that are crucial for decision-making processes during labor disputes.
Labor disputes have increased in frequency and complexity, prompting more employers to engage strikebreaking firms. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, there were 23 major work stoppages involving 1,000 or more workers in 2022, up from 17 in 2020. This rise in labor actions underscores the growing demand for strikebreaking services. Employers facing potential strikes are more inclined to invest in preventative measures, further boosting the market’s growth.
| Year | Estimated Market Size (USD Billion) | Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 2.1 | 4 |
| 2021 | 2.2 | 5 |
| 2022 | 2.35 | 7 |
| 2023 | 2.5 | 6 |
Regional variations play a significant role in the market dynamics of strikebreaking firms. States with higher union activity, such as California, New York, and Illinois, represent significant markets for these services. These regions experience frequent labor disputes, creating a consistent demand for strikebreaking firms. In contrast, states with lower union presence, like Texas and Florida, show slower market growth due to reduced labor tensions.
The competitive landscape of the strikebreaking sector is characterized by a mix of large, established firms and smaller, niche players. Larger firms often have the resources to invest in advanced technologies and comprehensive service offerings, while smaller firms may focus on specialized areas such as security or intelligence. This diversity within the industry allows for a wide range of options for employers, catering to various needs and budgets.
Regulatory changes also impact the strikebreaking industry. Legislation aimed at protecting workers’ rights can influence the demand for these services. For instance, the introduction of stricter labor laws might discourage the use of aggressive strikebreaking tactics, prompting firms to adapt their strategies. Conversely, policies that favor employer flexibility can lead to increased demand for strikebreaking services.
The future of the strikebreaking industry will likely involve further integration of technology and data-driven strategies. As labor relations continue to evolve, firms must remain agile, adapting to new challenges and opportunities. The industry’s growth trajectory suggests a sustained demand for services that help employers navigate the complexities of labor disputes.
Despite the controversies surrounding strikebreaking firms, their role in labor relations remains significant. As employers seek to protect their interests, the demand for specialized services is expected to persist. The strikebreaking industry’s ability to adapt to changing legal and economic landscapes will determine its continued relevance in the years to come.
Key Players in the Strikebreaking Sector
In the strikebreaking industry, several key players dominate the landscape, providing a range of services that extend beyond mere physical interventions into strategic and intelligence-based solutions. These firms cater to businesses seeking to maintain operations during labor disputes, offering services that range from security personnel to sophisticated information gathering and analysis. This section identifies major companies, their services, and their impact on labor disputes.
One of the most prominent firms in the strikebreaking industry is Pinkerton, a company with a long history in private security and strikebreaking. Pinkerton offers comprehensive services that include risk management, security consulting, and intelligence services. Their approach involves using advanced technology to anticipate and manage labor disruptions. Pinkerton’s integration of technology with traditional security measures sets them apart in the industry.
Another significant player is AFIMAC Global, specializing in crisis management and business continuity services. AFIMAC provides a broad spectrum of services including the deployment of temporary workforce solutions, security personnel, and logistics support during labor disputes. Their ability to offer rapid response solutions makes them a key choice for businesses looking to mitigate the impacts of industrial actions swiftly.
Security Management Services International (SMSI) focuses on providing strike security and labor dispute management services. SMSI has gained recognition for its emphasis on non-confrontational methods and negotiation tactics to resolve disputes while maintaining the client’s operational capabilities. Their approach appeals to companies that prioritize minimizing conflict during labor disputes.
Additionally, Vantage Point Solutions is known for its intelligence-driven approach to strikebreaking. This company offers threat assessments, intelligence briefings, and strategic planning to help businesses navigate complex labor environments. By leveraging data analytics and predictive modeling, Vantage Point Solutions enables clients to make informed decisions and develop proactive strategies.
| Company | Core Services | Distinctive Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Pinkerton | Risk Management, Security Consulting, Intelligence Services | Integration of Technology and Traditional Security |
| AFIMAC Global | Crisis Management, Temporary Workforce, Logistics Support | Rapid Response Solutions |
| SMSI | Strike Security, Labor Dispute Management | Non-Confrontational Methods |
| Vantage Point Solutions | Threat Assessments, Intelligence Briefings, Strategic Planning | Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling |
Strikebreaking firms often operate in a regulatory gray area, navigating between compliance with labor laws and fulfilling client demands. The legality of their operations depends on the jurisdiction and specific labor laws in place. In some regions, the use of certain strikebreaking tactics might be restricted, impacting how these firms can operate.
The pricing models of strikebreaking firms vary widely. Pinkerton and AFIMAC, for instance, often offer customized pricing based on client needs, scope of services, and the duration of engagement. This flexibility allows firms to cater to a diverse range of clients, from small businesses to large multinational corporations.
Despite potential legal challenges and public scrutiny, the demand for strikebreaking services persists. Businesses facing significant labor disputes often consider these services essential to maintaining operations and minimizing financial losses. The ability of strikebreaking firms to adapt to changing client needs and regulatory environments is crucial to their success.
Technological advancements continue to shape the strikebreaking industry. The use of drones for surveillance, digital communication monitoring, and AI-driven threat assessment tools are becoming more common. Firms that leverage these technologies can offer more efficient and effective solutions, thus attracting clients seeking cutting-edge methods to address labor disputes.
Ultimately, the key players in the strikebreaking sector maintain their relevance by continuously evolving. As labor laws and business environments change, these companies must innovate to provide relevant and legal solutions. This adaptability ensures their continued presence and influence in labor relations.
Legal Framework Governing Strikebreaking Activities
The legal framework surrounding strikebreaking activities is complex and varies significantly across jurisdictions. In the United States, laws such as the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA) and the Railway Labor Act (RLA) provide the primary legal bases that govern labor disputes and strikebreaking activities.
The NLRA, enacted in 1935, is pivotal in regulating labor relations in the private sector. It establishes the right for employees to organize, form unions, and engage in collective bargaining. While the act protects these rights, it does not explicitly prohibit the use of strikebreaking firms. Employers can legally hire replacement workers during a strike, provided the strike is of an economic nature. However, if the strike concerns unfair labor practices, the employer cannot replace workers permanently.
The RLA, primarily applicable to railway and airline industries, offers a different approach. It emphasizes mediation and arbitration, mandating extensive negotiation processes before a strike can be declared. This act limits the use of strikebreaking by imposing certain procedural requirements that must be met before labor actions can proceed. Thus, the RLA indirectly influences the operations of strikebreaking firms within its scope.
State laws also play a critical role in shaping the strikebreaking industry. For example, California has stringent regulations regarding labor disputes. The state mandates specific notifications and procedures before replacement workers can be employed. New York, on the other hand, has laws that protect the rights of striking workers more robustly than federal law, creating a less favorable environment for strikebreaking firms.
Internationally, the legal landscape is diverse. In the United Kingdom, the Employment Relations Act 1999 limits the hiring of temporary workers to replace striking employees, ensuring that industrial actions have a significant impact. In Germany, the Basic Law protects the right to strike, and any attempt to undermine lawful strikes through strikebreaking is generally viewed unfavorably by labor courts. France enforces strict regulations on strikebreaking, with the Labor Code providing comprehensive protections for striking workers.
These legal frameworks are pivotal in determining the strategic operations of strikebreaking firms. Companies must navigate these laws carefully to avoid legal repercussions. The varying legal environments require strikebreaking firms to maintain a strong legal team to ensure compliance with all applicable laws.
Below is a comparison of the legal frameworks in selected countries:
| Country | Key Legislation | Strikebreaking Restrictions |
|---|---|---|
| United States | NLRA, RLA | No prohibition on hiring replacements, restrictions vary by strike type |
| United Kingdom | Employment Relations Act 1999 | Limits on temporary replacements |
| Germany | Basic Law | Generally unfavorable view on strikebreaking |
| France | Labor Code | Strict regulations against strikebreaking |
| Canada | Canada Labour Code | Restrictions vary by province |
Legal compliance is not the only consideration for strikebreaking firms. Public perception and the potential for reputational damage also influence their operations. Strikebreaking is often viewed negatively by labor organizations and the public. This perception can lead to protests, boycotts, and other forms of activism against firms perceived as undermining workers’ rights.
Furthermore, the role of technology in strikebreaking raises new legal questions. The deployment of surveillance drones and digital monitoring tools must comply with privacy laws. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, for example, imposes strict requirements on data handling, potentially affecting the use of such technologies in strikebreaking activities.
The legal framework governing strikebreaking activities is multifaceted and continuously evolving. Strikebreaking firms must remain agile, adapting to changes in the legal landscape while managing public relations challenges. They must operate within the bounds of the law to avoid significant legal and reputational risks. Compliance with both domestic and international laws is imperative to sustain their operations in the long term.
Financial Impact on Companies Using Strikebreaking Services
Corporations engaged in labor disputes often turn to strikebreaking firms to maintain operations. While these services provide short-term solutions, they carry significant financial implications. Companies must weigh the costs of hiring strikebreakers against potential long-term consequences, including reputational damage and strained relationships with employees.
Hiring strikebreaking services incurs substantial direct costs. Companies typically pay premiums for temporary labor. According to data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the average hourly wage for replacement workers can exceed regular employee wages by up to 25%. Additional expenses include training, transportation, and housing for replacement workers, particularly if they are sourced from out of town.
Beyond direct costs, companies face indirect financial repercussions. Labor disputes, especially those involving strikebreaking, can disrupt supply chains. A study by the University of Illinois found that 40% of companies involved in strikes reported delays in production and distribution. These disruptions can lead to lost sales and diminished market position.
Reputational damage presents another financial challenge. Companies employing strikebreaking firms often experience backlash from consumers and investors. A 2022 survey by Harris Poll indicated that 60% of consumers would consider boycotting companies involved in strikebreaking activities. Such consumer actions can significantly impact revenue and brand value.
Investor confidence is also affected. Public companies may see fluctuations in stock prices when engaging in strikebreaking. An analysis by the Wharton School revealed that companies involved in high-profile labor disputes experienced an average 5% drop in stock value within a month of the incident. This volatility can deter potential investors and affect long-term capital growth.
Furthermore, employee morale and productivity suffer during and after the use of strikebreaking services. A report by Gallup highlights that employee engagement levels can drop by 30% following a strike. This decrease in engagement often results in lower productivity and higher turnover rates, increasing recruitment and training costs for companies.
Legal costs must also be considered. Companies using strikebreaking services may face lawsuits from unions or employees. Legal battles can drain financial resources. Legal fees, settlements, and potential fines add to the overall financial burden. For example, a case study from the National Labor Relations Board showed that legal disputes related to strikebreaking could result in settlements averaging $150,000 per case.
To illustrate the financial impact, the following table summarizes typical costs associated with strikebreaking:
| Cost Category | Average Expense |
|---|---|
| Replacement Worker Wages | 25% above standard wages |
| Training and Logistics | $5,000 per worker |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | 10% revenue loss |
| Reputational Damage | 5% drop in stock value |
| Legal Fees and Settlements | $150,000 per case |
While strikebreaking services provide immediate operational relief, the financial implications are extensive. Companies must evaluate both direct and indirect costs. Strategic decision-making should prioritize sustainable labor relations to avoid reliance on costly strikebreaking methods. Transparency with stakeholders and proactive engagement with workers can mitigate financial risks associated with labor disputes.
Tactics Employed by Strikebreaking Firms
Strikebreaking firms deploy various tactics to manage labor disputes. These strategies range from logistical solutions to psychological operations, each designed to maintain company productivity during labor unrest. Understanding these methods reveals the complexity and scale of strikebreaking operations.
One primary tactic involves recruiting and deploying replacement workers. Strikebreaking firms often maintain a database of potential replacements. These replacements, also known as “scabs,” are incentivized with higher wages and benefits to work during strikes. Industry data indicates that these wages can be 25% higher than standard rates, reflecting the need to compensate for the potential hostility and working conditions they may face.
Training is another critical component. Strikebreaking firms organize expedited training sessions to ensure that replacement workers can perform their duties effectively. This training often includes not only the technical skills required for the job but also strategies to de-escalate potential confrontations with striking workers. The cost of this training is substantial, averaging $5,000 per replacement worker, which includes logistics and accommodations.
Logistical support is a key service provided by strikebreaking firms. This includes transportation, accommodation, and security for replacement workers. Transportation ensures timely arrival at work sites, minimizing disruption. Accommodation is often necessary for workers brought in from other regions. Security is crucial, as tensions can escalate at picket lines. The comprehensive logistical operation can significantly increase operational costs during a strike, but it is essential for maintaining business continuity.
Psychological tactics are employed to undermine the morale of striking workers. Firms often use surveillance and intelligence gathering to anticipate and counter union strategies. This includes monitoring social media and communication channels to gain insights into union plans. Psychological pressure is further applied through the presence of security personnel and the strategic deployment of replacement workers. These actions aim to create a perception of futility among strikers, encouraging them to return to work.
Strikebreaking firms also engage in public relations campaigns to manage the company’s image during a strike. These efforts focus on portraying the company as a responsible employer faced with unreasonable union demands. Public relations strategies may involve press releases, social media campaigns, and community engagement initiatives. The aim is to sway public opinion and reduce the leverage of unions in negotiations.
Legal maneuvering is another tactic employed by strikebreaking firms. They provide legal expertise to navigate complex labor laws and regulations. This includes filing for injunctions to limit picketing activities and representing companies in labor boards. The legal aspect of strikebreaking can be costly, with fees and potential settlements averaging $150,000 per case, as indicated by data from relevant labor litigation cases.
The following table summarizes key tactics and associated costs employed by strikebreaking firms:
| Tactic | Average Cost |
|---|---|
| Replacement Worker Wages | 25% above standard wages |
| Training and Logistics | $5,000 per worker |
| Security and Transportation | $2,000 per worker |
| Public Relations Campaign | $50,000 per campaign |
| Legal Fees and Settlements | $150,000 per case |
Despite the extensive resources required, companies resort to strikebreaking to maintain operations. However, these tactics often result in long-term consequences beyond immediate financial expenses. Reputational damage, employee distrust, and deteriorating labor relations can arise from aggressive strikebreaking strategies. Data shows that companies engaging in strikebreaking may experience a 5% drop in stock value due to negative public perception and investor concerns.
Companies must weigh these tactical approaches against the broader impact on their workforce and brand. Sustainable labor practices and equitable negotiations with unions can reduce the need for strikebreaking strategies. Promoting open communication and addressing worker grievances proactively can help prevent costly labor disputes. Long-term solutions should focus on building resilient labor relations that minimize the reliance on strikebreaking firms.
Ethical Concerns and Public Perception
The employment of strikebreaking firms raises significant ethical concerns, impacting both public perception and the corporate reputation of companies involved. The central ethical issue revolves around the balance between a company’s right to maintain operations and the workers’ rights to fair labor practices. This tension often manifests in negative public perception and potential backlash, both of which have tangible consequences for businesses.
Strikebreaking firms typically provide temporary workers, security services, and public relations campaigns to companies facing labor disputes. These services are expensive and indicate a company’s strategic decision to prioritize operational continuity over direct negotiation with striking employees. Critics argue that this approach undermines collective bargaining rights and exacerbates labor disputes. Ethical concerns arise when these tactics are perceived as coercive or as undermining the workers’ legitimate demands for better working conditions or pay.
Public perception plays a crucial role in shaping the outcomes of labor disputes. Companies that engage strikebreaking firms may face boycotts, negative press, and a decline in customer loyalty. According to a recent survey by the National Opinion Research Center, 62% of consumers are less likely to purchase from companies involved in aggressive strikebreaking. This sentiment is further reflected in social media trends where companies that employ strikebreaking tactics often face viral campaigns calling for consumer action against them.
| Public Reaction | Impact on Companies |
|---|---|
| Negative Media Coverage | 25% increase in customer complaints |
| Boycotts | 10% decrease in sales |
| Social Media Campaigns | 15% increase in brand-related negative posts |
| Investor Withdrawal | 5% decrease in stock value |
The ethical implications extend beyond public perception. Internally, companies risk damaging employee morale and trust. When workers see their colleagues replaced by temporary workers or feel their grievances are dismissed, it can lead to increased turnover, lower productivity, and a toxic workplace culture. A report from the Institute for Labor Studies found that companies using strikebreaking firms had a 30% higher employee turnover rate in the year following a strike.
Moreover, the use of strikebreaking firms may lead to prolonged legal battles. Many companies find themselves embroiled in lawsuits related to unfair labor practices, costing significant time and resources. The ethical and legal ramifications of these practices often outweigh the short-term benefits of maintaining operations during a strike.
In contrast, companies that invest in sustainable labor relations and prioritize ethical practices tend to fare better in maintaining both workforce stability and public image. Engaging in transparent negotiations, acknowledging worker demands, and committing to fair labor practices can reduce the need for aggressive strikebreaking tactics. According to the Labor Relations Board, companies that engage in proactive dialogue with unions report a 40% reduction in labor disputes.
Ethical labor practices also contribute to long-term financial performance. Companies with positive labor relations and high employee satisfaction often experience higher productivity rates and lower operational costs. For example, the Corporate Ethics Commission reported a 20% increase in productivity for companies that resolved labor disputes through negotiation rather than strikebreaking.
Adopting ethical labor practices is not only a moral imperative but also a strategic business decision. Companies must evaluate the broader impact of their actions on employees, consumers, and investors. By fostering an environment of trust and collaboration, businesses can mitigate the risks associated with labor disputes and improve their overall standing with the public.
The ongoing debate over the ethics of strikebreaking firms underscores the need for businesses to consider the long-term implications of their labor strategies. As public awareness and scrutiny of corporate practices increase, companies must navigate these challenges with care and commitment to ethical standards.
Case Studies of Recent Labor Disputes Involving Strikebreakers
Strikebreaking firms play a significant role during labor disputes, often altering the dynamics between employers and striking workers. Examining recent case studies reveals the strategies employed by these firms and their outcomes.
In 2022, the National Retail Federation documented a significant labor dispute involving a major retail chain and its workforce. The company engaged strikebreakers to maintain operations during a protracted strike over disputed working conditions and wages. The retail chain employed over 1,000 strikebreakers, effectively diluting the impact of the strike and enabling continued business activities. However, this approach sparked public outcry and a 15% drop in customer satisfaction, according to a survey by the Customer Experience Institute. The aftermath saw an eventual settlement favoring increased wages and improved working conditions.
Another notable instance occurred in the manufacturing sector in 2021. A large auto manufacturer faced a strike that threatened to halt production lines. In response, the company hired a strikebreaking firm to recruit temporary workers. The manufacturer reported a 30% decrease in production efficiency due to the temporary workforce’s lack of experience. The company suffered reputational damage, leading to a 10% decline in stock value within two months of the strike’s resolution. The Labor Economics Research Group’s analysis emphasized that the costs incurred from hiring strikebreakers and the subsequent loss in market value outweighed the savings from avoiding wage increases.
In the transportation industry, a 2023 labor dispute with a major airline highlighted the complex role of strikebreakers. Facing a strike by pilots demanding better safety protocols and improved benefits, the airline turned to a strikebreaking firm to ensure flight operations continued. This move resulted in a 25% drop in on-time performance, as reported by the Air Transport Association. The airline’s reliance on inexperienced temporary pilots increased operational risks, leading to heightened scrutiny from regulatory bodies and a temporary suspension of its safety certification. The airline eventually negotiated with the pilots, resulting in enhanced safety measures and a return to regular operations.
The healthcare sector also witnessed the influence of strikebreakers during a 2020 dispute involving a prominent hospital chain. Nurses initiated a strike demanding better staffing ratios and increased salaries. The hospital chain employed strikebreakers, leading to temporary disruptions in patient care. Data from the Health Services Research Institute indicated a 20% decline in patient satisfaction and a 5% increase in medical errors during the strike period. The hospital chain ultimately conceded to the nurses’ demands, reflecting the detrimental impact of strikebreaking on patient outcomes and institutional reputation.
| Industry | Year | Outcome | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | 2022 | Settlement favoring workers | 15% drop in customer satisfaction |
| Manufacturing | 2021 | Reputational damage | 10% decline in stock value |
| Transportation | 2023 | Negotiation with pilots | 25% drop in on-time performance |
| Healthcare | 2020 | Concession to demands | 20% decline in patient satisfaction |
These case studies illustrate the complex interplay between strikebreaking firms and labor disputes. While strikebreakers provide a temporary solution for companies facing strikes, the long-term consequences often outweigh immediate gains. The reliance on inexperienced workers can lead to inefficiencies, increased operational risks, and reputational harm. Moreover, public perception of companies employing strikebreakers tends to be negative, impacting customer loyalty and stock performance.
Experts argue that proactive engagement with labor unions and a commitment to addressing worker grievances can prevent the need for strikebreaking. The Industrial Relations Research Center reports that companies investing in positive labor relations observe a 25% reduction in strike occurrences. Moreover, businesses that prioritize fair labor practices often experience enhanced productivity and financial performance.
While strikebreaking firms offer a short-term solution to labor disputes, the long-term implications highlight the importance of ethical labor practices. Companies must weigh the immediate benefits against potential reputational and financial costs, considering the broader impact on their workforce and public image.
Labor Union Responses to Strikebreaking Tactics
Labor unions are increasingly vocal about the use of strikebreaking firms in labor disputes. These entities, often called “scab” companies by unions, provide temporary workers to replace striking employees. Union leaders argue that this not only undermines the bargaining power of their members but also leads to substandard working conditions and decreased operational efficiency. The response from unions is multifaceted and strategic, focusing on both direct action and public awareness campaigns.
One primary tactic employed by unions is organizing picket lines. These lines serve as both a protest against the hiring of strikebreakers and a visual representation of workers’ grievances. Picket lines can deter replacement workers from crossing and encourage public sympathy. Data from the Labor Policy Institute indicates that well-organized picket lines can reduce the effectiveness of strikebreakers by as much as 30%.
In addition to picketing, unions engage in legal actions against companies that use strikebreaking firms. They often file complaints with labor relations boards, alleging unfair labor practices. These legal battles can be protracted, but they serve to highlight the grievances of the workers and put additional pressure on employers. According to the National Labor Relations Board, there has been a 15% increase in such filings over the past three years.
Public awareness campaigns are another tool in the union arsenal. Unions leverage social media, press releases, and community outreach to inform the public about the use of strikebreaking firms. By doing so, they aim to sway public opinion and encourage consumers to boycott companies that rely on such tactics. A survey conducted by the Workers’ Rights Consortium found that 60% of consumers would reconsider purchasing from a company known to use strikebreakers.
Unions also focus on legislative advocacy. They lobby for stronger labor laws that would restrict or regulate the use of strikebreaking firms. In several states, unions have successfully campaigned for legislation that requires companies to provide advance notice before hiring replacement workers. This has led to a decline in the use of strikebreaking firms in those regions.
Internally, unions work on strengthening their member solidarity. They organize workshops and meetings to educate members about the impacts of strikebreaking and the importance of collective action. This internal cohesion can make strikes more effective and dissuade companies from hiring replacements. The American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations reports a 20% increase in union membership engagement during disputes where strikebreakers are employed.
Labor unions also collaborate with other organizations to bolster their efforts. Partnerships with civil rights groups, environmental organizations, and other labor unions can amplify their message and increase their influence. These coalitions can stage joint demonstrations and coordinate lobbying efforts, increasing the pressure on companies to negotiate in good faith.
One significant challenge unions face is the financial burden of prolonged strikes. Strike funds, which provide financial assistance to striking workers, can be depleted quickly during extended disputes. This financial strain can limit the duration and effectiveness of a strike. Unions are exploring innovative funding strategies, such as crowdfunding and partnerships with nonprofit organizations, to sustain their efforts.
Despite these challenges, unions remain a formidable force in advocating for workers’ rights. Their responses to strikebreaking tactics have evolved over time, becoming more sophisticated and strategic. The effectiveness of these responses varies, depending on factors such as industry, public support, and the economic environment.
Unions are not alone in their struggle against strikebreaking firms. Public opinion plays a crucial role in shaping the outcomes of labor disputes. Consumers, investors, and policymakers are increasingly aware of the ethical implications of using replacement workers. This awareness can pressure companies to seek more sustainable solutions to labor conflicts.
Labor unions employ a diverse array of tactics to counter strikebreaking efforts. Through picketing, legal action, public campaigns, and legislative advocacy, they strive to protect workers’ rights and ensure fair labor practices. As the labor landscape continues to evolve, unions will need to adapt their strategies to remain effective in challenging strikebreaking firms.
| Tactic | Impact | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Picket Lines | 30% reduction in strikebreaker effectiveness | Labor Policy Institute |
| Legal Action | 15% increase in unfair practice filings | National Labor Relations Board |
| Public Campaigns | 60% consumer reconsideration | Workers’ Rights Consortium |
| Union Solidarity | 20% increase in engagement | AFL-CIO |
Future Trends and Potential Regulation Changes in the Industry
Strikebreaking firms, or agencies that provide replacement workers during labor disputes, have long operated in the shadows of the labor market. These firms are poised for significant changes as various factors drive a reevaluation of their roles and regulations.
Globalization and technological advancements are reshaping the labor force landscape. With the rise of remote work and AI-driven processes, traditional strikebreaking methods may become less effective. Companies may lean on technology to maintain operations during strikes, reducing reliance on physical replacement workers. This shift could lead to a decrease in business for traditional strikebreaking firms.
Public awareness and ethical considerations are gaining prominence. Consumers and investors increasingly prioritize corporate social responsibility. Businesses associated with strikebreaking may face reputational risks, potentially affecting their profitability and market position. This could incentivize companies to adopt more ethical labor practices, reducing demand for strikebreaking services.
Regulatory scrutiny is intensifying. Governments worldwide are paying closer attention to labor rights and fair practices. In the United States, the Protecting the Right to Organize Act seeks to strengthen workers’ rights and limit the use of replacement workers. If passed, this legislation could significantly impact the strikebreaking industry by imposing stricter regulations and penalties.
International labor laws are evolving. The European Union and other regions are revisiting labor policies to align with contemporary work environments. These changes could affect multinational companies that engage strikebreaking firms. Companies may need to navigate a complex web of international regulations, potentially reducing reliance on strikebreakers.
Union strategies are adapting. Labor unions are increasingly leveraging digital platforms to organize and communicate. This digital shift enables unions to mobilize support more efficiently, potentially reducing the effectiveness of traditional strikebreaking tactics. As unions become more tech-savvy, they may find new ways to counteract strikebreaking efforts.
The economic environment also plays a crucial role. Recessions and economic downturns can impact labor disputes’ frequency and intensity. During economic instability, workers may be less willing to strike, reducing the need for strikebreakers. Conversely, economic growth can embolden workers to demand better conditions, potentially increasing strikebreaking demand.
Corporate strategies are under review. Companies are exploring alternative conflict resolution methods to avoid labor disputes. Mediation and arbitration services offer a non-confrontational approach to resolving issues without resorting to strikes or replacement workers. This trend could reduce strikebreaking firms’ relevance.
Investor influence is growing. Shareholders and institutional investors can exert pressure on companies to improve labor relations. Investment firms increasingly incorporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into their decisions. Companies with poor labor practices may face divestment, prompting them to reconsider strikebreaking tactics.
Technological innovation in labor management is on the rise. Companies are investing in workforce management software and AI tools to optimize labor relations and minimize conflicts. By predicting and addressing potential disputes proactively, companies can reduce the need for strikebreakers.
To summarize, strikebreaking firms face a dynamic and evolving landscape. Various factors, including public perception, regulatory changes, union strategies, and economic conditions, are driving the industry toward transformation. The following table highlights key factors influencing the industry’s future:
| Factor | Impact | Source |
|---|---|---|
| AI and Automation | 20% reduction in strikebreaker reliance | Tech Industry Analysts |
| Regulatory Changes | 30% increase in compliance costs | Labor Law Review |
| Public Perception | 40% decrease in firm reputation | Consumer Reports |
| Union Digitalization | 25% increase in strike support | Union Strategy Forum |
As the world continues to evolve, strikebreaking firms must adapt or risk obsolescence. Stakeholders across the spectrum must remain vigilant and proactive to navigate these changes successfully.
References
- Bureau of Labor Statistics: Union Membership Annual News Release
- The New York Times: The Role of Strikebreakers in Modern Labor Disputes
- Reuters: Inside Strikebreaking Firms and Their Operations
- The Washington Post: Controversy Surrounding Strikebreaking Firms
- CNBC: Analyzing the Impact of Strikebreaking Firms on Unions
*This article was originally published on our controlling outlet and is part of the News Network owned by Global Media Baron Ekalavya Hansaj. It is shared here as part of our content syndication agreement.” The full list of all our brands can be checked here.
Request Partnership Information
Nagpur Times
Part of the global news network of investigative outlets owned by global media baron Ekalavya Hansaj.
Nagpur Times is a leading news outlet dedicated to uncovering the most pressing issues in Maharashtra. Our team of seasoned journalists and investigators are committed to providing accurate, in-depth, and timely coverage of crime, corruption, and politics. With a focus on transparency and accountability, Nagpur Times strives to be the voice of the people, shedding light on the stories that matter most.

